Power supply plays a vital role in Electronic Gadgets and equipment. The most common form is takes AC from mains and gives output as DC power as per requirement of the circuit to run by it.
The output of the power supply is measured as output Voltage and the output Current.
Basics of Power Supply
A DC power supply is basically an AC to DC converter known as Rectifier. In most power supplies there are number of different elements including Rectifier.
These may not all be present in each and every design.
Transformer:
A transformer is used to transform the voltage level of mains according to required voltage. Mostly it requires low voltage then the mains voltage, So it is a step-down transformer.
Two types of secondary winding are used in power supply.
Single secondary:
In this transformer a single winding is there for stepdown voltages. The voltage rating is printed on it as 0-12/500, 0-6/500, 0-9/750 etc. This shows the voltage and current rating of the transformer. For example 0-12/500 means if its primary is connected to 230 Volts then its secondary voltage will be 12 Volts and it can deleiver 500 mAmps max.This transformer is used with full-wave bridge rectifier circuit. These transformers
Half-wave Rectifier:
The operation of a half wave rectifier is simple. To understand it you should know that how a diode works? A Diode conducts current only when it is forward biased. The same principle is used in a half wave rectifier to convert AC to DC. The input we give here is an AC current. This input voltage is stepped down to desired voltage using a transformer. The reduced voltage is fed to the diode and load resistance RL.
During the positive half cycles of the AC, the diode will be forward biased and during the negative half cycles of AC, the diode will be reverse biased. Since the diode passes current only during one half cycle of the input wave, we get an output as shown in diagram. The output is positive and significant during the positive half cycles of input wave. At the same time output is zero or insignificant during negative half cycles of input wave. This is called half wave rectification.
This rectifier circuit is not so widely used as it requires a center tapped transformer. Its operation is also The basic circuit is outlined below
During the positive half cycle of the supply, diodes D3 and D4 conducts as they are in forward biased while diodes D1 and D2 are reverse biased and the current flows through the load as shown below
Smoothing: The pulsating DC from the rectifier not a usable form. It falls to zero when the AC waveform crossed the zero axis, and then rising to its peak. A filtering capacitor is used to smooth the pulsating DC. This gives us 99% pure DC. Large value capacitors are normally used for this purpose.

Pin-out of the 7805 regulator IC.
Dual Power Supply Circuit


A DC power supply is basically an AC to DC converter known as Rectifier. In most power supplies there are number of different elements including Rectifier.
These may not all be present in each and every design.
Transformer:
A transformer is used to transform the voltage level of mains according to required voltage. Mostly it requires low voltage then the mains voltage, So it is a step-down transformer.
Two types of secondary winding are used in power supply.
Single secondary:
In this transformer a single winding is there for stepdown voltages. The voltage rating is printed on it as 0-12/500, 0-6/500, 0-9/750 etc. This shows the voltage and current rating of the transformer. For example 0-12/500 means if its primary is connected to 230 Volts then its secondary voltage will be 12 Volts and it can deleiver 500 mAmps max.This transformer is used with full-wave bridge rectifier circuit. These transformers
Center Tapped:
In center Tapped transformer there are three wires at the secondary. The center wire is known as center taping. It voltage rating is as 6-0-6/500, 12-0-12/500, 7.5-0-7.5/1000 etc. For example 12-0-12/500, it shows that the voltage accross center taping and any one of the side wire is 12 Volts & voltage across side wires is 24 Volts. Current rating is 500 mAmps max.
Rectifier:
The Rectifier converts the incoming AC format into pulsating DC. Basically two types of rectifier may be used, half wave or full
wave.
Half-wave Rectifier:
The operation of a half wave rectifier is simple. To understand it you should know that how a diode works? A Diode conducts current only when it is forward biased. The same principle is used in a half wave rectifier to convert AC to DC. The input we give here is an AC current. This input voltage is stepped down to desired voltage using a transformer. The reduced voltage is fed to the diode and load resistance RL.
During the positive half cycles of the AC, the diode will be forward biased and during the negative half cycles of AC, the diode will be reverse biased. Since the diode passes current only during one half cycle of the input wave, we get an output as shown in diagram. The output is positive and significant during the positive half cycles of input wave. At the same time output is zero or insignificant during negative half cycles of input wave. This is called half wave rectification.
Two Diode Full-wave Rectifier:
This rectifier circuit is not so widely used as it requires a center tapped transformer. Its operation is also The basic circuit is outlined below
Full-wave Bridge Rectifier:
The Positive Half-cycle
The four diodes labelled D1 to D4 are arranged in “series pairs” with only two diodes conducting current during each half cycle. During the positive half cycle of the supply, diodes D1 and D2 conducts as they are in forward biased while diodes D3 and D4 are reverse biased and the current flows through the load as shown below

During the positive half cycle of the supply, diodes D3 and D4 conducts as they are in forward biased while diodes D1 and D2 are reverse biased and the current flows through the load as shown below
Smoothing: The pulsating DC from the rectifier not a usable form. It falls to zero when the AC waveform crossed the zero axis, and then rising to its peak. A filtering capacitor is used to smooth the pulsating DC. This gives us 99% pure DC. Large value capacitors are normally used for this purpose.
Full-wave Rectifier with Smoothing Capacitor
_____________________________________________________________________________________
The performance of each and every electronic circuit depends upon the power supply that energizes the circuit. It provides required current & Voltage to the circuit. Any disturbance or noise in the power supply affects in working of circuit. If there is any fluctuation in voltage of power supply the circuit may not only work properly but also can be damage permanently.
There are two types of power supplies
1) Unregulated power supply
2) Regulated power supply
Unregulated supply is used in circuits where there is variation in load current & voltage is permissible up to some level. The supply voltage affected by increase in load current. Because in such supply
1) The output voltage reduces as load current increases
2) The ripple in output voltage increases as load current increases
So this kind of supply can not be used where there is noticeable change in load current frequently. But although many circuits works on unregulated supply because it requires very few components and design is also very simple. Also some fluctuation in supply level can be tolerated due to load current change. The regulated power supply is required in digital circuits, the circuits in which the components can not tolerate even 1% change in supply level like micro controller, micro processor etc.
So here I am giving the procedure to design regulated power supply that means which components should be chosen to have required regulated output voltage with required current. The procedure requires calculations based on some designing equations, some assumptions and approximations that we must take during designing.
Positive Voltage Regulator
This circuit 78xx/79xx regulator chip is used as voltage regulator. In 78xx ic xx is denotes the output voltage of the regulator. for example 7805 for 5V, 7809 for 9V amd 7812 for 12V.
in the ic no. 78xx ic 78 is for positive voltage and 79 for negative voltage.
7905 for -5V, 7912 for -12V etc.
Pin-out of the 7805 regulator IC.
Component list
7805 regulator IC
100 uF electrolytic capacitor, at least 25V voltage rating
10 uF electrolytic capacitor, at least 6V voltage rating
100 nF ceramic or polyester capacitor
If you need more than 150 mA of output current, you can update the output current up to 1A doing the following modifications:
- Change the transformer from where you take the power to the circuit to a model which can give as much current as you need from output
- Put a heatsink to the 7805 regulator (so big that it does not overheat because of the extra losses in the regulator)
Other output voltages
If you need other voltages than +5V, you can modify the circuit by replacing the 7805 chips with another regulator with different output voltage from regulator 78xx chip family. The last numbers in the the chip code tells the output voltage. Remember that the input voltage muts be at least 3V greater than regulator output voltage ot otherwise the regulator does not work well.
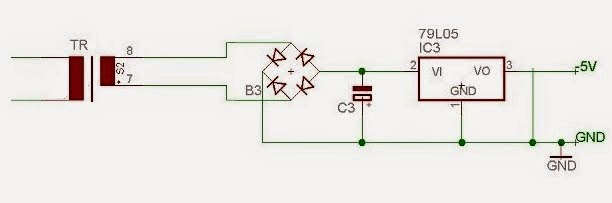 |
-5V Power Supply Circuit |
-5V Power Supply Circuit |
Dual Power Supply Circuit
Regulated variable Power Supply
Some times we need variable voltage source so that we can change the output voltage of the power supply, the simplest form of the variable power supply is we can connect a variable resistor for changing output voltage directly to output of the rectifier, but this configuration has very low efficiency. And output is also unregulated. affected by load current.
For an efficient variable and regulated output voltage we can use another IC know as variable voltage regulator.
IC no. is LM317.
This is a circuit of a variable power supply. LM317 is a very common IC comes in TO-220 package. It requires only few external parts to make a variable power supply. Input voltage is from 3 volt to 40 volt DC and output voltage is DC 1.2V to 37V adjustable and the output current is 1.5A. But the circuit mentioned below will deliver output voltage from 1.2V to 15V with 1.5A.
| PARTS LIST | |
| R1 | 220 Ω |
| R2 | 2.2 K Variable Resistor |
| C1 | 3300 µf 50v |
| C2 | 10 µf 25v |
| C3 | 1 µf 25v |
| C4 | 0.1 µf |
| D1 | 1N4007 Rectifier Diodes - 4 |
| D2 | IN4007 |
| D3 | IN4007 |
| IC1 | LM317 |
| T1 | 9-0-9 V 500mA Transformer |
| F | 500mA |
The diodes D2 and D3 in the circuit used to prevent damage to the regulator during certain adverse conditions. It might be rare but protection can save the cost of a new regulator.









No comments:
Post a Comment